Table of Contents
Introduction
While low-pass filtering (LPF) is ubiquitous high pass filters (HPF) can be needed depending on the RF environment or for specific algorithms. The previous post FIR Low Pass Filter Design with Remez demonstrated how to use the remez() function in the SciPy package to design LPF filter weights. The following blog will demonstrate how to use remez() to design a high pass filter as well as designing LPF filters and upconverting them.
Additional examples for Remez filter design can be found in the SciPy documentation under “Examples”.
More blog posts on filter design:
Design a High Pass Filter with Remez
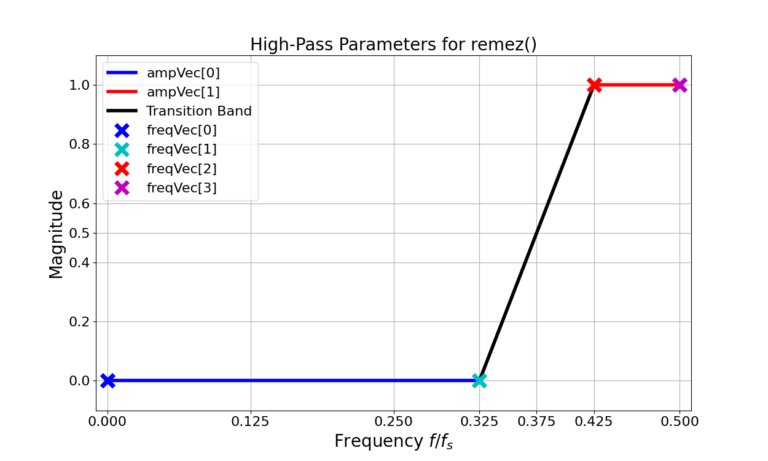
A HPF can be designed directly with remez() using the following code:
import scipy.signal
filterLength = 21
cutoff = 0.375
transBand = 0.1
fPass = cutoff - (transBand/2)
fStop = cutoff + (transBand/2)
freqVec = [0, fPass, fStop, 0.5]
ampVec = [0, 1]
HPFRemez = scipy.signal.remez(filterLength,freqVec,ampVec)
The design is similar to that of the LPF discussed in this blog post with the differences being in the cutoff frequency and amplitude vector.
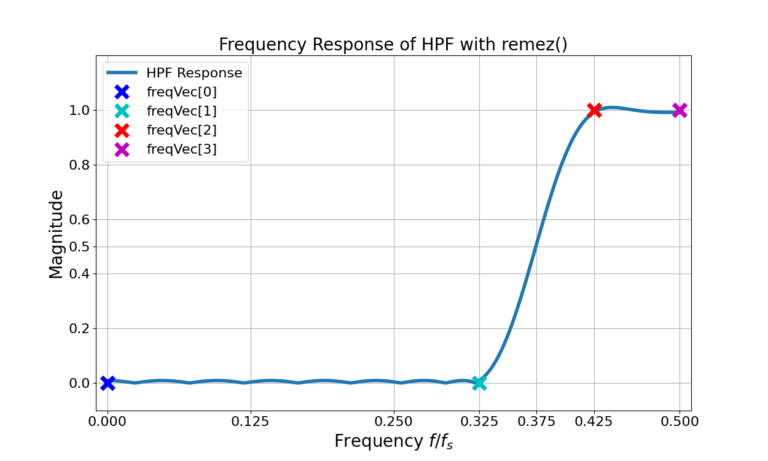
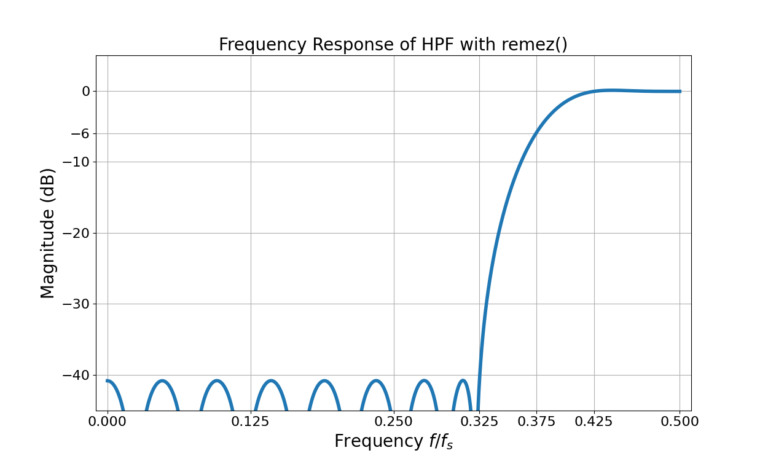
The HPF parameters passed into the remez() function are given in Figure 1, the resulting frequency response in Figure 2 and the magnitude in dB in Figure 3.
Upconvert Low Pass Filter to High Pass Filter
An alternative to designing a HPF directly is to design an LPF and then upconvert the filter weights by multiplication with a sinusoid,
(1) ![]()
To make the LPF into a HPF it must be upconverted with a center frequency of ![]() , or in radians
, or in radians ![]() , therefore
, therefore
(2) ![]()
(3) ![]()
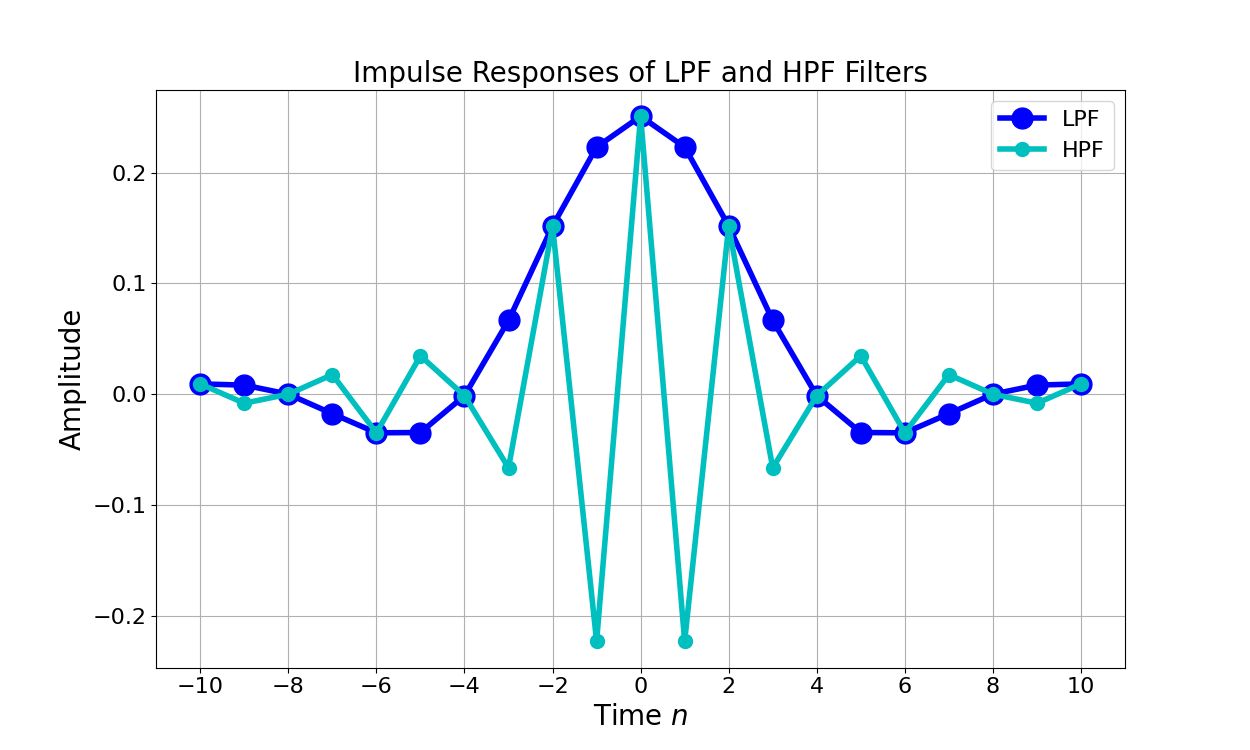
Figure 4 gives the impulse response for an LPF and the upconverted HPF.
Frequency Domain Analysis of LPF Upconversion to HPF
The discrete-time Fourier transform of (1) is the frequency-domain convolution of the filter weights ![]() and
and ![]() ,
,
(4) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{equation*}\begin{split}H_{HPF}\left(e^{j\omega}\right) & = \mathcal{F} \{ h_{LPF}[n] \cdot cos(\phi n) \} \\& = \mathcal{F} \{ h_{LFP}[n]] \} \ast \mathcal{F} \{ cos(\phi n) \}, \\& = H_{LPF}\left(e^{j\omega}\right) \ast \mathcal{F} \{ cos(\phi n) \},\end{split}\end{equation*}](https://www.wavewalkerdsp.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c8d7b30e06c2e92890e26f37a993606c_l3.png)
where ![]() is convolution. From (2), conveniently
is convolution. From (2), conveniently
(5) ![]()
The discrete-time Fourier transform of a sequence ![]() multiplied by a complex exponential is [oppenheim1999, p.59]
multiplied by a complex exponential is [oppenheim1999, p.59]
(6) ![]()
Substituting ![]() , the Fourier transform (4) can then be written
, the Fourier transform (4) can then be written
(7) ![]()
which is the low-pass filter response frequency shifted to ![]() or
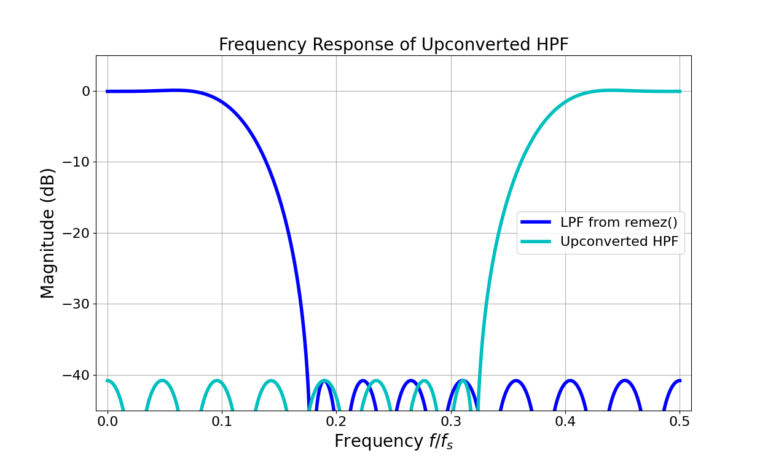
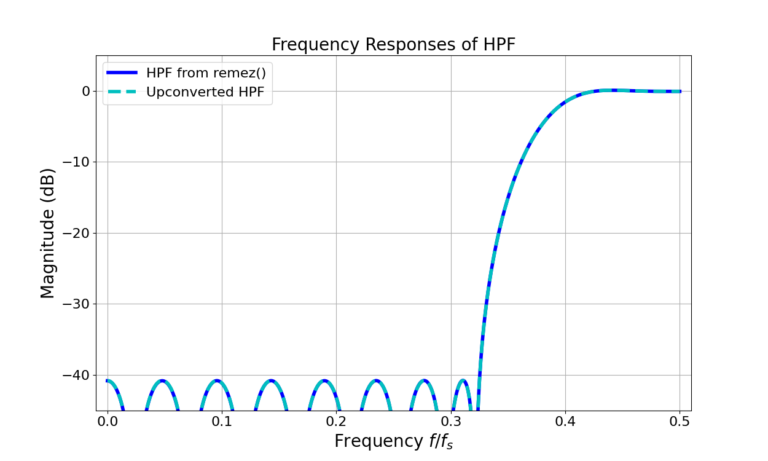
or ![]() radians. Figure 5 gives the magnitude of the frequency response in (7) and Figure 6 shows the Remez-designed HPF magnitude frequency response is identical to that of the upconverted HPF.
radians. Figure 5 gives the magnitude of the frequency response in (7) and Figure 6 shows the Remez-designed HPF magnitude frequency response is identical to that of the upconverted HPF.
Conclusion
A HPF can be designed directly using the remez() function by passing in the appropriate frequency vector and amplitude vector. Alternatively an LPF can be designed and then upconverted to become a HPF through with
(8) ![]()
Have you seen these blogs on filter design?
![Figure 1: The two sequences for the autocorrelation of x0[n] and x0[n].](https://www.wavewalkerdsp.com/wp-content/uploads/wordpress-popular-posts/5515-featured-125x100.png)