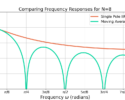
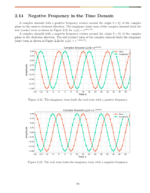
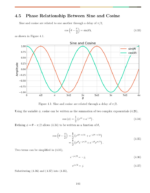
The Fourier transform ![]() is linear such that
is linear such that
(1) ![]()
The Fourier transform of ![]() is
is
(2) ![]()
As the integral is a linear operator the Fourier transform of the summation can be written as the summation of two Fourier transforms,
(3) ![]()
therefore
(4) ![]()
If you liked this post please check out the List of Important Math for DSP!